Compound exercises for the chest are an integral part of any strength training or bodybuilding regimen. These multi-joint movements not only target the pectoral muscles but also engage numerous other muscle groups, making them highly efficient for building overall upper body strength and power.
Incorporating compound exercises into your chest workouts can lead to significant gains in muscle mass, strength, and functional fitness. Whether you’re a novice looking to improve your chest development or an experienced lifter aiming to maximize your training efficiency, understanding and implementing compound exercises for the chest is crucial for achieving your fitness goals.
What are Compound Exercises for Chest?
Compound exercises for the chest are multi-joint movements that engage multiple muscle groups, including the pectoral muscles, triceps, and shoulders. These exercises are known for their efficiency in targeting the upper body, promoting strength, and muscle growth.
Some popular compound chest exercises include the barbell bench press, incline bench press, dumbbell bench press, push-ups, and chest dips. Incorporating these exercises into your workout routine can lead to balanced muscle development and enhanced functional strength.
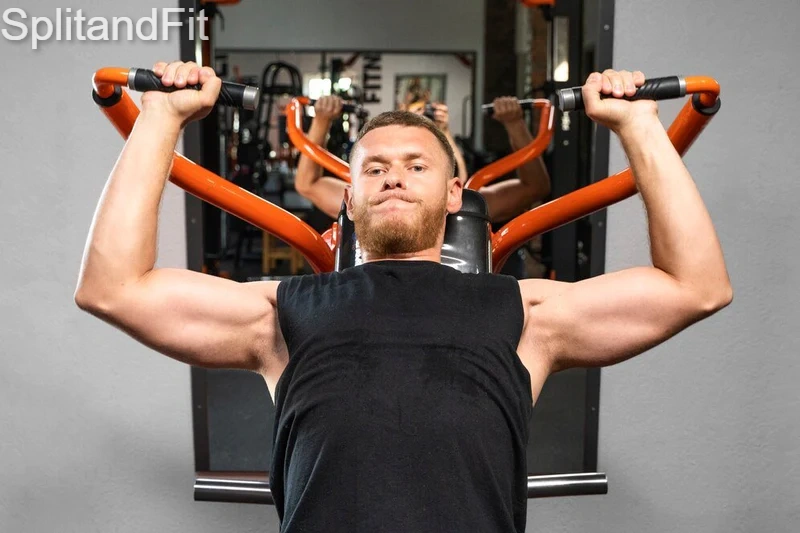

Benefits Of Chest Compound Exercises
Here are the key benefits of incorporating compound exercises for the chest:
- Efficiency: Compound chest exercises engage multiple muscle groups, allowing for a more comprehensive workout in less time.
- Strength and Muscle Development: These exercises promote overall upper body strength and muscle development, targeting not only the pectoral muscles but also the triceps and shoulders.
- Functional Fitness: By engaging various muscle groups simultaneously, compound exercises for the chest contribute to enhanced functional strength and power.
- Caloric Expenditure: These exercises elevate the heart rate, contributing to increased caloric expenditure and potential weight management benefits.
- Balanced Muscle Activation: Incorporating compound chest exercises can lead to balanced muscle development, contributing to improved aesthetics and overall physical performance.
- Cardiovascular Training Benefit: Some compound exercises elevate the heart rate, providing a cardiovascular training benefit in addition to strength training.
These points highlight the significance of compound exercises for the chest, showcasing their multifaceted benefits for individuals aiming to improve their upper body strength, muscle development, and overall fitness levels.
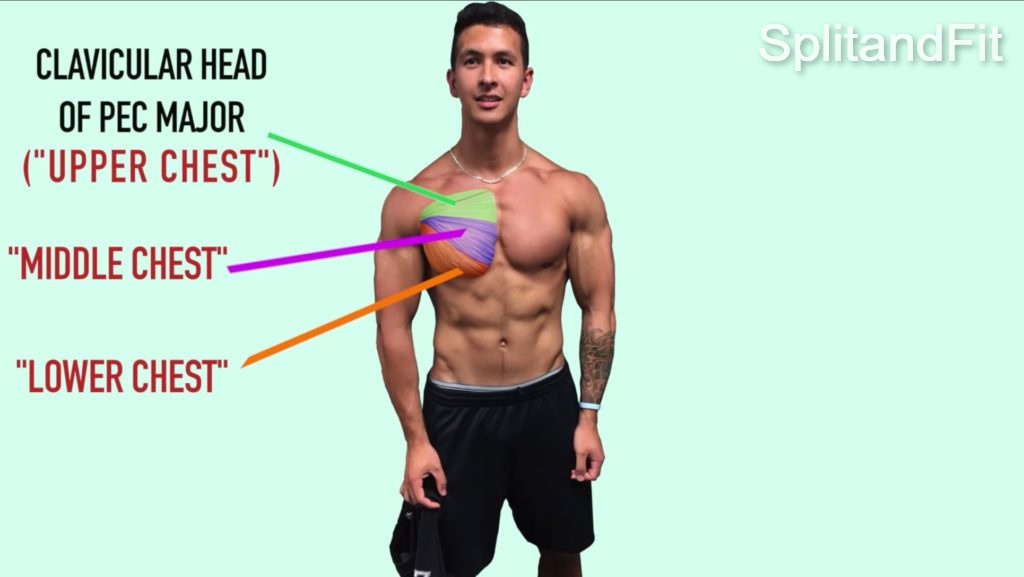
Muscles Targeted By the Compound Chest Exercises
The following are the primary muscles targeted by compound chest exercises:
- Pectoralis Major: The pectoralis major, often referred to as the chest muscle, is the primary targeted muscle in compound chest exercises. It contributes to movements such as pushing and arm adduction.
- Triceps Brachii: While not the primary focus, compound chest exercises also engage the triceps brachii, aiding in elbow extension during pressing movements.
- Anterior Deltoids: The front portion of the deltoid muscles in the shoulders is activated during compound chest exercises, contributing to shoulder flexion and stabilization.
- Serratus Anterior: This muscle, located on the side of the chest beneath the armpit, is engaged to stabilize the shoulder blades during pressing movements, aiding in overall stability.
- Coracobrachialis: This smaller muscle in the upper arm assists in shoulder flexion and horizontal adduction, contributing to the overall movement pattern during compound chest exercises.
Highlighting these targeted muscles underscores the comprehensive nature of compound chest exercises, emphasizing their ability to engage multiple muscle groups for a well-rounded upper-body workout.
Top Compound Exercises for Chest
Here are the top 10 bodyweight exercises for wrestling:
- Push-ups: A versatile compound exercise that activates the chest, shoulders, and triceps, making it an effective bodyweight option.
- Incline Bench Press (Barbell): This variation targets the upper chest and shoulders, contributing to a well-rounded chest workout.
- Dumbbell Bench Press: Provides unilateral movement and engages the stabilizing muscles in addition to targeting the chest.
- Dips: Engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps, promoting strength and muscle development.
- Barbell Bench Press: A classic compound exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Dumbbell Floor Press: This exercise emphasizes the chest muscles and provides a unique movement pattern compared to traditional bench presses.
- Landmine Chest Presses: Offers a different angle of movement, distinctly engaging the chest and shoulders.
- Weighted Chest Dips: Engages the chest and triceps, offering an effective bodyweight exercise for upper body strength.
- Chest Press Machine: Provides a guided range of motion to target the chest muscles and is suitable for individuals seeking controlled resistance.
- Decline Bench Press: Targets the lower portion of the chest, contributing to balanced development across the entire chest region.
These exercises are backed by science and have been recommended as effective compound movements for targeting the chest and upper body muscles.
1. Push-Ups
Push-ups are a fundamental bodyweight exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core muscles. This versatile exercise can be performed anywhere without the need for equipment, making it an effective way to develop upper body strength and muscular endurance.
How to Perform:
- Start in a prone position on the floor, with your hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart and aligned with your mid-chest.
- Extend your legs behind you, creating a straight line from your head to your heels, and engage your core muscles to maintain a stable body position.
- Lower your body towards the floor by bending your elbows, keeping them close to your sides at a 45-degree angle.
- Descend until your chest is just above the ground or as far as your strength allows while maintaining a straight back and proper form.
- Push yourself back up to the starting position by fully extending your arms, focusing on using your chest and triceps to drive the movement.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while ensuring proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Maintain a neutral spine and avoid sagging or arching your back during the movement.
- Keep your head in line with your spine and gaze slightly forward to maintain proper neck alignment.
- Engage your core muscles throughout the exercise to stabilize your body and prevent excessive hip sagging.
- Modify the push-up position based on your fitness level, such as performing knee push-ups or incline push-ups, to gradually progress towards standard push-ups.
Performing push-ups with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core muscles, contributing to overall upper body strength and muscular endurance.
2. Incline Bench Press (Barbell)
The incline bench press with a barbell is a compound exercise targeting the upper portion of the chest, shoulders, and triceps. This exercise involves lifting a barbell while reclined on an incline bench, providing an effective way to develop upper chest strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Set an adjustable bench to an incline of around 30-45 degrees.
- Lie down on the bench with your back flat against it, feet planted firmly on the ground.
- Grip the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, ensuring a comfortable and stable grip.
- Unrack the barbell and hold it directly above your chest with arms fully extended.
- Lower the barbell in a controlled manner towards your upper chest, keeping your elbows at a slight angle from your body.
- Pause briefly at the bottom of the movement, then push the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Focus on maintaining a stable and firm position on the bench throughout the exercise.
- Ensure smooth and controlled movement both during the lowering (eccentric) and lifting (concentric) phases.
- Engage the chest and shoulder muscles to drive the movement, avoiding excessive arching of the lower back.
- Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise and aim for progressive overload to stimulate muscle growth.
Performing the incline bench press with proper technique and control can effectively target the upper chest muscles and contribute to overall upper body strength and development.
3. Dumbbell Bench Press
The dumbbell bench press is a fundamental compound exercise that primarily targets the chest muscles, while also engaging the shoulders and triceps. It involves lifting a pair of dumbbells in a controlled manner, providing an effective way to develop chest strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Sit on the edge of a flat bench with the dumbbells resting on your thighs.
- Lie back on the bench, using your thighs to help propel the dumbbells up to the starting position.
- Hold the dumbbells directly above your chest with arms fully extended, palms facing forward (neutral grip).
- Lower the dumbbells towards the sides of your chest, keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Pause briefly once the dumbbells are parallel to your chest, then push them back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Keep your feet planted firmly on the ground for stability and engage your core muscles to maintain a neutral spine position.
- Focus on a smooth and controlled movement, avoiding rapid or jerky motions.
- Ensure that both dumbbells move symmetrically and avoid any uneven distribution of weight.
- Aim to maintain a balanced grip and wrist position throughout the exercise to minimize strain on the wrists and maximize chest engagement.
Performing the dumbbell bench press with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest muscles and contribute to overall upper body strength and development.
4. Barbell Bench Press
The barbell bench press is a quintessential compound exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It involves lifting a barbell while lying on a flat bench, providing an effective way to develop overall upper body strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Lie down on a flat bench with your back pressed firmly against it, feet planted on the ground.
- Grip the barbell with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, ensuring a secure and stable grip.
- Unrack the barbell and hold it directly above your chest with arms fully extended.
- Lower the barbell in a controlled manner towards your mid-chest, keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle from your body.
- Pause briefly once the barbell lightly touches your chest, then push it back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Maintain a stable and firm position on the bench throughout the exercise, with your shoulder blades retracted.
- Engage your chest, shoulders, and triceps to drive the movement, avoiding excessive arching of the lower back.
- Focus on smooth and controlled movement during both the lowering (eccentric) and lifting (concentric) phases.
- Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise and aim for progressive overload to stimulate muscle growth.
Performing the barbell bench press with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest muscles and contribute to overall upper body strength and development.
5. Dips
Dips are a challenging compound exercise that primarily targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. This bodyweight exercise involves lowering and lifting the body using parallel bars or a dip station, providing an effective way to develop upper body strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Stand between the parallel bars or grasp the handles of a dip station with your arms fully extended.
- Hoist yourself up, supporting your body with locked elbows and a straight torso.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows and leaning slightly forward, allowing your elbows to flare out to the sides.
- Descend until your shoulders are below your elbows or until you feel a deep stretch in your chest and shoulders.
- Push yourself back up to the starting position by straightening your arms, focusing on using your chest and triceps to drive the movement.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Keep your core engaged and maintain a neutral spine position throughout the exercise.
- Control the movement to avoid swinging or jerking motions, focusing on smooth and controlled descent and ascent.
- Adjust the width of your grip to target different areas of the chest and shoulders. A wider grip may emphasize chest activation, while a narrower grip can engage the triceps more.
- Gradually increase the difficulty by adding weight using a dip belt once bodyweight dips become manageable.
Performing dips with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to overall upper body strength and development.
6. Dumbbell Floor Press
The dumbbell floor press is a compound exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps while providing stability and reducing stress on the shoulders. This exercise involves pressing a pair of dumbbells while lying on the floor, making it an effective way to develop upper body strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Lie on the floor with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground, holding a dumbbell in each hand at chest level.
- Position the dumbbells so that your upper arms are in contact with the floor, creating a stable base.
- Press the dumbbells upward, fully extending your arms while keeping your elbows in line with your shoulders.
- Lower the dumbbells back down in a controlled manner until your upper arms make contact with the floor again.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while ensuring proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Focus on maintaining a stable and neutral spine position throughout the exercise.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize the body and minimize excessive arching of the lower back.
- Control the movement to ensure smooth and controlled pressing and lowering of the dumbbells.
- Adjust the weight of the dumbbells based on your strength and comfort level, gradually increasing the load as you progress.
Performing the dumbbell floor press with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to overall upper body strength and development.
7. Landmine Chest Presses
Landmine chest presses are a dynamic compound exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps while incorporating core stabilization. This exercise involves pressing a barbell attached to a landmine unit, providing a unique and effective way to develop upper body strength and muscle mass.
How to Perform:
- Position the end of a barbell into the landmine unit or secure it in a corner to create a pivot point.
- Stand facing away from the landmine and hold the other end of the barbell with both hands at chest level.
- Step forward to create tension in the barbell and assume a stable stance with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Press the barbell away from your chest, fully extending your arms while engaging the chest and shoulders.
- Slowly bring the barbell back towards your chest in a controlled manner, maintaining stability and control throughout the movement.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while focusing on proper form and controlled movement.
Tips:
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize the body and minimize excessive movement during the exercise.
- Control the movement to ensure smooth and controlled pressing and returning of the barbell.
- Maintain a stable and neutral spine position throughout the exercise to minimize strain on the lower back.
- Adjust the weight of the barbell based on your strength and comfort level, gradually increasing the load as you progress.
Performing landmine chest presses with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to overall upper body strength and development.
8. Weighted Chest Dips
Weighted chest dips are an advanced variation of the traditional dips, targeting the chest, shoulders, and triceps while incorporating added resistance for muscle development. This exercise involves using a dip belt or weighted vest to increase the load during the dip movement, providing an effective way to further challenge upper body strength and muscle growth.
How to Perform:
- Secure a dip belt around your waist or wear a weighted vest, ensuring that the additional weight is evenly distributed.
- Stand between the parallel bars or grasp the handles of a dip station with your arms fully extended and the added weight secured.
- Hoist yourself up, supporting your body with locked elbows and a straight torso.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows and leaning slightly forward, allowing your elbows to flare out to the sides, while carrying the added resistance.
- Descend until your shoulders are below your elbows or until you feel a deep stretch in your chest and shoulders, maintaining control throughout the movement.
- Push yourself back up to the starting position by straightening your arms, focusing on utilizing your chest and triceps to drive the movement, while managing the increased resistance.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions with proper form and control, ensuring that the added weight does not compromise the technique.
Tips:
- Engage your core muscles to maintain stability and control while carrying the additional resistance.
- Control the movement to avoid swinging or jerking motions, focusing on smooth and controlled descent and ascent.
- Gradually increase the added weight as your strength improves, aiming for progressive overload to stimulate muscle adaptation.
- Ensure proper recovery and rest periods between weighted dip sessions to allow for muscle repair and growth.
Performing weighted chest dips with proper technique and control, while gradually increasing the resistance, can effectively enhance the development of the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to overall upper-body strength and muscle hypertrophy.
9. Chest Press Machine
The chest press machine is a popular resistance training equipment designed to target the chest, shoulders, and triceps while providing stability and support. This exercise involves pushing weight forward using a guided motion, making it an effective way to develop upper body strength and muscle endurance.
How to Perform:
- Adjust the seat height and position on the chest press machine to align the handles with your mid-chest level.
- Sit on the machine with your back against the backrest, feet flat on the floor, and grasp the handles with a firm grip.
- Press the handles forward by extending your arms, fully engaging the chest and shoulder muscles.
- Slowly bring the handles back towards your body in a controlled manner, maintaining stability and control throughout the movement.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while focusing on proper form and controlled movement.
Tips:
- Adjust the weight stack according to your strength and comfort level, ensuring proper resistance for the exercise.
- Keep your back firmly against the backrest and maintain a stable seated position throughout the movement.
- Control the movement to ensure smooth and controlled pressing and returning of the handles.
- Adjust the grip width to target different areas of the chest and shoulders, allowing for variation in muscle engagement.
Performing the chest press machine exercise with proper technique and control can effectively target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to overall upper body strength and muscle development.
10. Decline Bench Press
The decline bench press is a compound exercise that primarily targets the lower portion of the chest, along with the triceps and shoulders. This exercise involves pressing a barbell or dumbbells while lying on a decline bench, providing an effective way to develop strength and muscle mass in the lower chest region.
How to Perform:
- Position yourself on the decline bench, securing your feet in place and lying back so that your head is lower than your hips.
- Grip the barbell or hold the dumbbells with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, ensuring a secure and stable grip.
- Unrack the barbell or dumbbells and hold them directly above your chest with arms fully extended.
- Lower the barbell or dumbbells in a controlled manner towards the lower chest, keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle from your body.
- Pause briefly once the barbell or dumbbells lightly touch your chest, then push them back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Perform the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Tips:
- Maintain a stable and firm position on the decline bench throughout the exercise, with your shoulder blades retracted.
- Engage your chest, shoulders, and triceps to drive the movement, avoiding excessive arching of the lower back.
- Focus on smooth and controlled movement during both the lowering (eccentric) and lifting (concentric) phases.
- Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the exercise, aiming for progressive overload to stimulate muscle growth in the lower chest region.
Performing the decline bench press with proper technique and control can effectively target the lower chest muscles and contribute to overall upper body strength and development.
Frequent Question Answers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is a compound exercise for the chest? | Compound chest exercises engage multiple muscle groups, such as the barbell bench press and push-ups. |
| What are the only 4 chest exercises? | The common 4 chest exercises are barbell bench press, dumbbell bench press, chest dips, and incline bench press. |
| Is chest press a compound? | Yes, the chest press is a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups in the chest, shoulders, and arms. |
| Should I do 3 chest exercises? | Incorporating 3 chest exercises can provide a well-rounded workout, targeting different areas of the chest muscles. |
| Are 7 exercises enough for chest? | 7 exercises can offer a comprehensive chest workout, but the effectiveness depends on individual fitness goals and workout intensity. |
| What is the number 1 chest exercise? | The barbell bench press is often regarded as one of the top chest exercises due to its effectiveness in targeting the chest, shoulders, and triceps. |
| Can I do chest every day? | It is not recommended to train the same muscle group, including the chest, every day to allow for proper recovery and muscle growth. |
| Are 3 compound exercises enough? | Including 3 compound chest exercises can contribute to a balanced and efficient workout targeting the chest and upper body. |
| How do bodybuilders train chest? | Bodybuilders often incorporate a variety of chest exercises, focusing on both compound movements and isolation exercises to target different areas of the chest musculature. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, compound exercises for the chest offer a multitude of benefits, including efficient engagement of multiple muscle groups, promoting overall upper body strength and muscle development, contributing to functional fitness, balanced muscle activation, and potential cardiovascular training benefits.
The targeted muscles include the pectoralis major, triceps brachii, anterior deltoids, serratus anterior, and coracobrachialis, providing a comprehensive upper body workout. By incorporating a variety of compound chest exercises, individuals can achieve well-rounded chest development and enhanced functional strength.






Leave a Reply